This is a question often raised, particularly in the face of conflicting information online.
So let’s explore the concept of diabetes remission, the scientific evidence supporting it, and practical steps to achieve it.
Understanding Diabetes Remission
Diabetes remission is indeed a real phenomenon, and can be achieved by people with type 2 diabetes.
Remission is defined as having an HbA1c level of less than 6.5% without the use of glucose-lowering medications for at least three months.
HbA1c is a blood test that measures your average blood glucose levels over the past two to three months. An HbA1c level of 6.5% or higher is indicative of diabetes, so a level below this threshold signifies improved blood sugar control.
LISTEN TO THE PODCAST
The History and Evolution of the Concept
Historically, type 2 diabetes was viewed as a progressive disease, inevitably leading to worsening health, increased medication use, and severe complications. This grim outlook began to change when studies started to explore the potential for remission. The first notable mention of diabetes remission in scientific literature came in 2009, with surgical interventions such as bariatric surgery showing promise.
However, it wasn’t until the publication of the Direct Study in 2017 that diet-induced remission gained significant attention. This study demonstrated that an intensive weight loss program could lead to diabetes remission. As a result, the conversation shifted towards understanding that type 2 diabetes might not always progress and could be managed or even halted through lifestyle changes.
Achieving Remission: Surgery vs. Diet
There are primarily two paths to achieving diabetes remission: surgical and dietary interventions.
- Surgical Intervention: Bariatric surgery, or weight loss surgery, has shown effectiveness in inducing diabetes remission. It significantly reduces calorie intake and alters hormonal signals related to hunger and blood sugar regulation. While effective, surgery comes with risks and should be considered a last resort after exploring other options.
- Dietary Intervention: Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in managing and potentially reversing type 2 diabetes. Two types of diets have been shown to be effective, very low calorie diets and low carb diets.
Very Low-Calorie Diets: These diets restrict daily calorie intake to 600-800 calories. While they can be effective, very low calorie diets are difficult to maintain long-term and should be undertaken under medical supervision due to potential health risks.
Low Carbohydrate Diets: Low carb diets, which include keto and more moderate low carb approaches, limit carbohydrate intake to varying degrees. Keto diets typically restrict carbs to under 50 grams per day, while low carb diets allow for 50-129 grams per day. A healthy low carb diet is effective for blood sugar control and weight loss and is generally more sustainable than a very low calorie diet or keto.
The Realistic Path to Remission
A low carb diet is the most practical and sustainable approach for achieving and maintaining diabetes remission. This approach does not require starvation or extreme restriction and can be integrated into daily life without significant disruption.
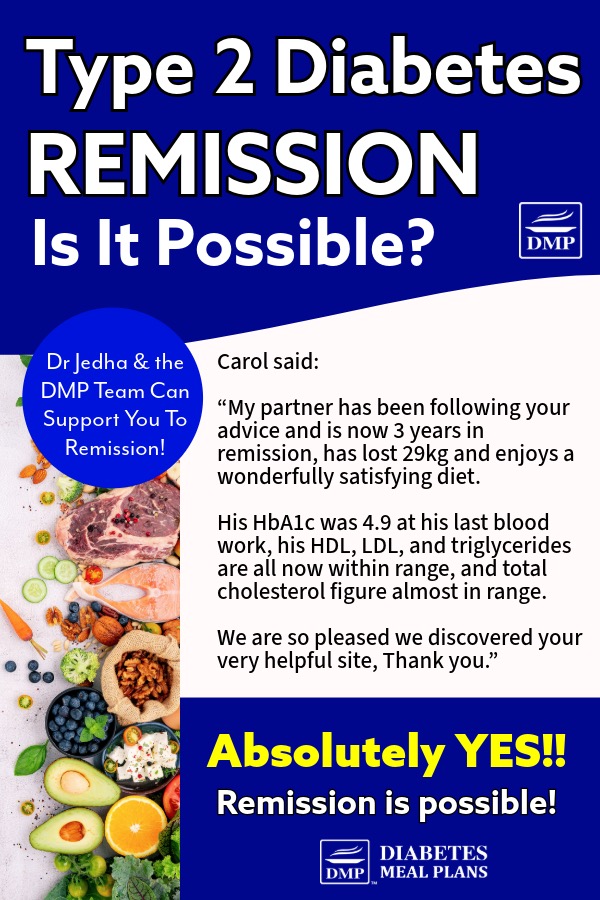
Here at DMP, we’ve been advocating for low carb eating for over a decade, helping many people achieve and sustain diabetes remission.
For instance, Carol’s husband, who has been in remission for three years, lost 29 kg and maintains excellent blood sugar levels and overall health through our healthy low carb eating approach.
Factors Influencing Remission
Several factors can influence your chances of achieving diabetes remission:
- Early Intervention: The sooner you take proactive steps after a diabetes diagnosis, the better your chances of remission.
- Weight Loss: Losing a significant amount of weight, around 10-15 kg, can significantly improve your chances of remission.
- Sustained Healthy Eating: Adopting a sustainable, balanced, low carb diet can help you maintain weight loss and blood sugar control.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes remission is possible and achievable for many. It requires a commitment to healthy eating, lifestyle changes, and often, a supportive program to guide you.
At DMP, we’ve seen countless success stories and are here to support you on your journey to better health and diabetes remission!